Evaluating Your RAG Components
In the previous section of this tutorial we've built a RAGAgent that:
- Retrieves documents related to a query from our knowledge base
- Generates natural sounding answers to the query from the retrieved context
To evaluate a RAG QA Agent, we'll use single-turn LLMTestCases from deepeval. We need to provide the retrieval_context in our test cases for evaluating our RAG application.
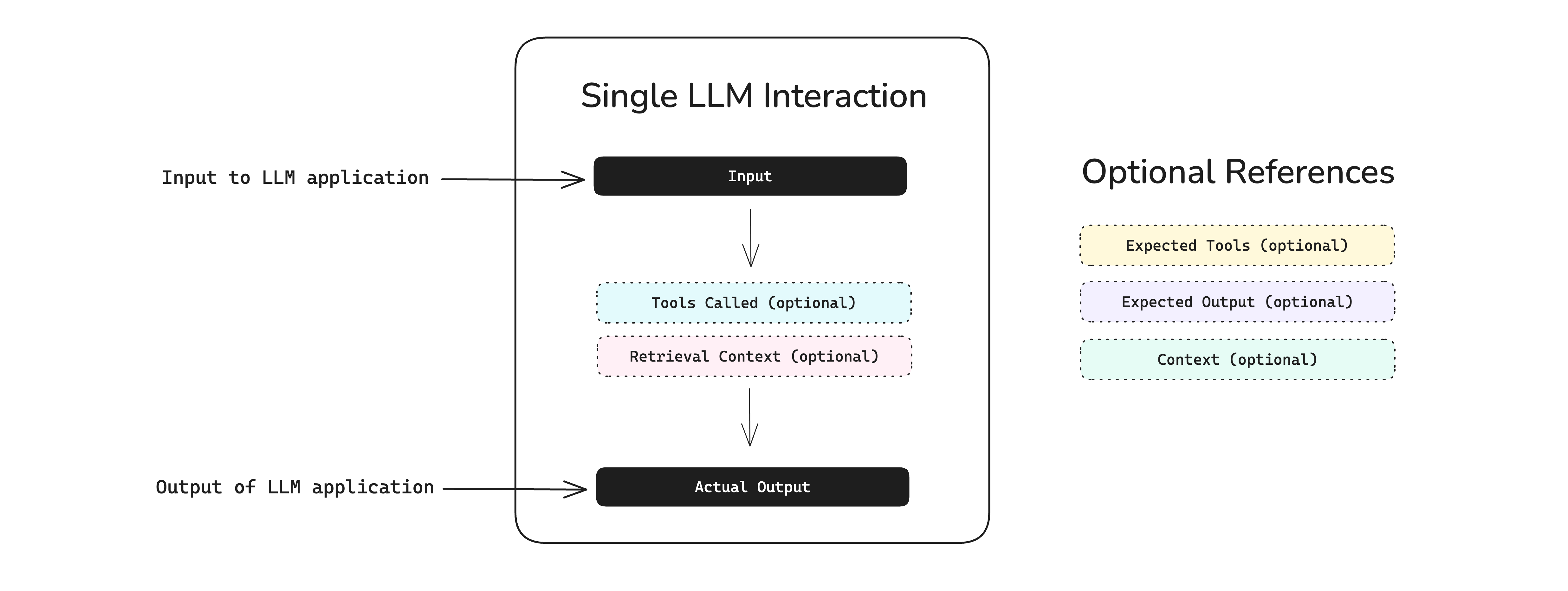
Our RAG agent first retrieves context from our knowledge base and uses the retrieved context to answer the question. All these questions are individual interactions that only depend on the retrieved context. Hence, we'll create our test cases with input, actual_output and retrieval_context as shown below:
from deepeval.test_case import LLMTestCase
test_case = LLMTestCase(
input="...", # Your query
actual_output="...", # The answer from RAG
retrieval_context="..." # Your retrieved context
)
When evaluating RAG based applications, you don't want to evaluate it on a random set of queries. You will have to create questions and queries that test the RAG application's abilities on edge cases that are in and outside your knowledge base.
Setup Testing Enviroment
There are 2 primary approaches to evaluating RAG based applications. They are:
-
Using Historical Data - You can pull datasets that contain previous queries or input queries that are frequently asked to your RAG agent.
-
Generate question-answer pairs - You can generate synthetic question-answer pairs from your knowledge base using AI.
Option 2 is the most recommended approach as it creates a ground truth for you to evaluate your RAG agent on. Creating synthetic data also allows you to create question-answer pairs on edge cases that you would never think of otherwise. While this approach is recommended we will still go through the other option quickly:
Use Historical Data
If you have queries and inputs stored in your database, you can convert them to LLMTestCase objects:
from deepeval.test_case import LLMTestCase
# Example: Fetch queries and responses from your database
queries = fetch_queries_from_db() # Your database query here
test_cases = []
for query in queries:
test_case = LLMTestCase(
input=query["input"],
actual_output=query["response"],
retrieval_context=query["context"]
)
test_cases.append(test_case)
print(test_cases)
This method is the quickest because the data already exists, however it might not be feasible becuase you may or may not store the retrieval context in your database. It also provides insights from the pevious knowledge base and does not represent your current RAG agent's capabilities. Hence, this is not recommended.
Generate QA Pairs
It is highly recommended to generate synthetic question-answer pairs using deepeval's Synthesizer. Because this allows you to:
- Generate question answer pairs that test your RAG application on edge cases
- Create a dataset with these QA pairs that allow you to use them anytime and anywhere
Here's how you can use the synthesizer:
from deepeval.synthesizer import Synthesizer
synthesizer = Synthesizer()
goldens = synthesizer.generate_goldens_from_docs(
# Provide the path to your documents
document_paths=['theranos_legacy.txt', 'theranos_legacy.docx', 'theranos_legacy.pdf']
)
This above code snippet returns a list of Goldens, that contain input and expected_output. We can use these goldens to create LLMTestCases by calling our RAG QA agent. Before that we need to store these goldens in a dataset to be able to use them later on.
Click here to learn more about Goldens in DeepEval
A dataset can only be created with a list of goldens. Goldens represent a more flexible alternative to test cases in the deepeval, and it is the preferred way to initialize a dataset using goldens. Unlike test cases, Goldens:
- Don't require an
actual_outputwhen created - Store expected results like
expected_outputandexpected_tools - Serve as templates before becoming fully-formed test cases
We can use the above created goldens to initialize a dataset and store it in cloud. Here's how you can do that:
from deepeval.dataset import EvaluationDataset
dataset = EvaluationDataset(goldens=goldens)
dataset.push(alias="RAG QA Agent Dataset")
✅ Done. We can now move on to creating test cases using this dataset.
You can learn more about how to use and customize the synthesizer here.
For RAG applications, it is recommended to evaluate your application on a component level for retriever, generator and as a whole RAG too.
Creating Test Cases
We will now use our RAG QA agent on the dataset to generate some LLMTestCases that we can use to evaluate our agent. We will create them using the inputs in goldens of our dataset and the agent's responses as actual_outputs.
from deepeval.test_case import LLMTestCase
from deepeval.dataset import EvaluationDataset
from rag_qa_agent import RAGAgent # Import your RAG Agent here
dataset = EvaluationDataset()
dataset.pull("RAG QA Agent Dataset")
agent = RAGAgent()
test_cases = []
for golden in dataset.goldens:
retrieved_docs = agent.retrieve(golden.input)
response = agent.generate(golden.input, retrieved_docs)
test_case = LLMTestCase(
input=golden.input,
actual_output=str(response),
retrieval_context=retrieved_docs,
expected_output=golden.expected_output
)
test_cases.append(test_case)
print(len(test_cases))
✅ Done. We can now move on to creating metrics for evaluating our RAG on a component level and as a whole.
Creating Your Metrics
Here are the metrics and evaluation criteria we'll be using to evaluate our RAG application.
Retriever Metrics
For a retriever deepeval provides 3 metrics to evaluate the quality of the retrieved context. Here are the metrics and the criteria they evaluate on:
- Contextual Relevancy — The retrieved context must be relevant to the query
- Contextual Recall — The retrieved context should be enough to answer the query
- Contextual Precision — The retrieved context should be precise and must not include unnecessary details
Here's how you can create these metrics:
from deepeval.metrics import (
ContextualRelevancyMetric,
ContextualRecallMetric,
ContextualPrecisionMetric,
)
relevancy = ContextualRelevancyMetric()
recall = ContextualRecallMetric()
precision = ContextualPrecisionMetric()
Generator Metrics
For a generator, we will have to define criteria based on the use case, in our case the QA agent will respond to us in json format, and hence we will be using a custom metric to evaluate the following criteria:
- Answer Correctness — To evaluate only the answer from our
json. - Citation Accuracy — To evaluate the citations mentioned in the
json.
These are custom criteria so we'll be using GEval metric to create these metrics. Here's how we will initialize our generator metrics:
from deepeval.metrics import GEval
answer_correctness = GEval(
name="Answer Correctness",
criteria="Evaluate if the actual output's 'answer' property is correct and complete from the input and retrieved context. If the answer is not correct or complete, reduce score."
evaluation_params=[LLMTestCaseParams.INPUT, LLMTestCaseParams.ACTUAL_OUTPUT, LLMTestCaseParams.RETRIEVAL_CONTEXT]
)
citation_accuracy = GEval(
name="Citation Accuracy",
criteria="Check if the citations in the actual output are correct and relevant based on input and retrieved context. If they're not correct, reduce score."
evaluation_params=[LLMTestCaseParams.INPUT, LLMTestCaseParams.ACTUAL_OUTPUT, LLMTestCaseParams.RETRIEVAL_CONTEXT]
)
We can now use the test cases and metrics we've created to run evaluations on our RAG agent.
Running Your First Evals
We will do separate evaluations for our retriever and generator. Here's how we can do that:
Retriever Evaluation
Now we can use the goldens we just created to evaluate the retriever. Here's how we can evaluate our retriever using the relevancy, recall and precision metrics that we've defined above:
from deepeval import evaluate
retriever_metrics = [relevancy, recall, precision]
evaluate(test_cases, retriever_metrics)
Generator Evaluation
We can use the exact same goldens to evaluate our generator by using the generator metrics we've defined above. Here's how we can evaluate the generator:
from deepeval import evaluate
generator_metrics = [answer_correctness, citation_accuracy]
evaluate(test_cases, generator_metrics)
🎉 Congratulations! You've successfully learnt how to:
- Create test cases during run time using datasets
- Run evaluations on the test cases using
deepeval
You can also run deepeval view to see the results of evals on Confident AI:
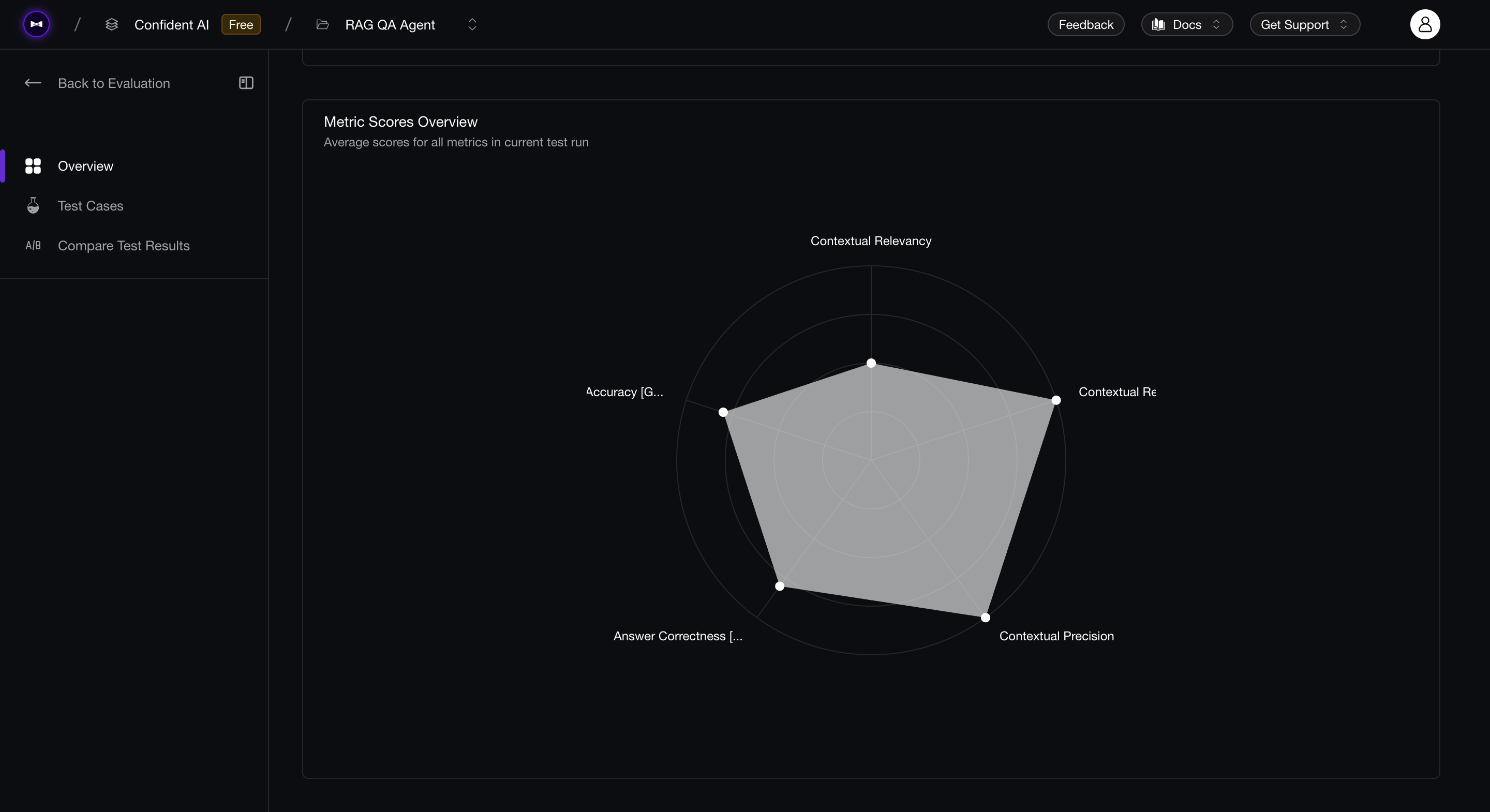
If you remember the implementation of our RAG agent. There are too many hyperparameters that can change the behavious of our RAG application. Click here to see the implementation of RAG Agent once again.
In the next section, we'll see how we can improve the performance of our RAG agent by tweaking hyperparameters and using the evaluation results.